We have been overwhelmed with the high quality applicants to the Bowdish lab but unfortunately we will not be taking on new graduate students for the 2026/27 academic year. Best of luck with your search.
Author Archives: Dr. Dawn M. E. Bowdish
Is dementia a vaccine preventable condition? Video now available.
The Bowdish lab is not accepting undergraduate or graduate students for the 2026/27 academic year
Thank you so much for your interest in our lab, but unfortunately we are full to the rafters and cannot take on any more students. If you are a Canadian student/permanent resident with a CGS or equivalent scholarship, you can reach out, but we have no unfunded positions in the foreseeable future.
Dr. Bowdish discusses measles elimination on TVO’s ‘The Rundown’
Dr. Bowdish is a panelist at the National Vaccine Summit on Adult Vaccination.
| Over the past 50 years, immunizations have saved more lives in Canada than any other health intervention. With the help of a doctor, an immunologist, a pharmacist and a patient advocate, Zoomer Radio’s Liz West leads this discussion about vaccines – what’s available, where and why we need them. |
| National Vaccine Summit |
| ‣ Recommended Vaccines & How To Get Them ‣ Navigating Provincial Health Systems ‣ The Role Your Pharmacist Can Play ‣ Emerging Science ‣ Fighting Disinformation & Vaccine Fatigue |
The Bowdish lab is not accepting applications from graduate students at this time.
Thank you for your interest in our lab but we are not accepting students for the 2025/26 academic year and are unlikely to take new graduate students in the 2026/27 academic year. Best of luck with your search.
The Bowdish lab is not accepting undergraduate or graduate students for 2025/2026
Unfortunately the lab is full and we cannot take any more students or volunteers for the 2025/26 academic year. Best of luck with your search.
Publication: “Rationalizing recommendations for influenza and COVID-19 vaccines”
Supplementary Tables and references
Bluesky Explainer here.
I’m excited to share our review “Rationalizing recommendations for influenza and COVID-19 vaccines”, which we feel makes a strong case for universal influenza and COVID-19 vaccination policies. With almost 500 references & 8 supplementary tables it’s a beast so let me break it down for you….1/n
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264410X25010722#ec0005
We started this >a year ago after conversations with immunologists, policy-makers, and the general public. We felt there were misunderstandings about how well COVID-19 vaccines work. We argue that they work as well or better than influenza vaccines so vaccination policies should be similar. 2/n
Like influenza, everyone but newborns has been exposed to COVID-19 through either vaccination or infection so we only reviewed studies in the post-Omicron/post-vaccine era. There is no doubt that the burden of disease has changed in the Omicron/vaccine era, but does that mean COVID is over? 3/n
Comparable data is hard to find, but when we looked at 2022/23 & 2023/24 data we see that deaths are still higher for COVID than influenza BUT looking at % hides the fact that COVID-19 is more contagious and in 23/24 there were almost 3x as many COVID hospitalizations than influenza. 4/n
There’s a common belief that COVID-19 vaccines don’t provide very good protection against symptomatic infection -is this true? These data are very, very hard to compile because the pace of variant replacement and vaccine changes has been dizzying 5/n
Before we get to the data – I just want to give a huge shoutout to @belongia.bsky.social for leading so many high quality studies on influenza effectiveness – look how easy to compare year-to-year. 6/n
Now look at how complicated it is to compare COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness. In influenza studies it is often possible to assess which strain a person was infected with so you can assess vaccine effectiveness by strain. COVID-19 vaccines are almost never matched with the circulating variants.. 7/n
…but despite that disadvantage, levels of protection from symptomatic infection and severe disease are similar between COVID & influenza vaccines. Note that protection against symptomatic infection is VERY hard to estimate because people who don’t get sick don’t get tested. 8/n
There has been some frustration that COVID-19 vaccines don’t last longer but neither does protection from either infection or vaccination for other viruses. When we compare protection < 3 months and > 3 months, COVID-19 vaccines look pretty good, esp considering rapid variant change 9/n
We also make a case to increase to increase the range of vulnerable populations. Canada has been a leader in including congregate living and equity-deserving groups in priority populations (#elbowsup !) but people living with lung and heart issues should be included 10/n.
Vaccine programs are decided by more than efficacy and efficacy – here’s a summary of what the National Advisory Council on Immunization (Canada) includes. Our review doesn’t address the programmatic, cost, and social considerations, which are also important. 11/n
There are still a lot of unknowns, but we feel strongly that universal & free COVID-19 and influenza vaccines would be a good investment in health, health systems, and attendance at work and school. Thank you to the brilliantly detail oriented Dr.@jabreznik.bsky.social and infl Dr Matt Miller Fin!
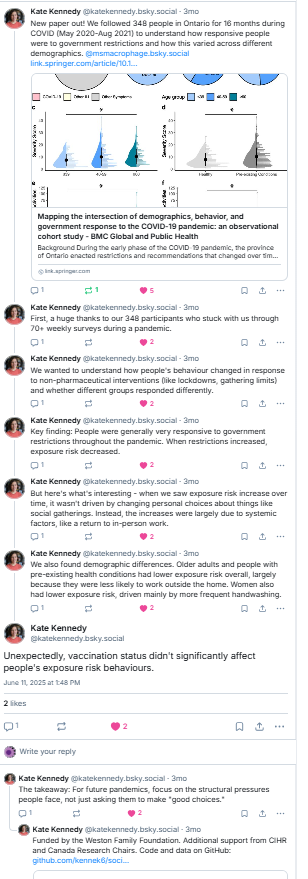
Publication: “Mapping the intersection of demographics, behavior, and government response to the COVID-19 pandemic: an observational cohort study”
Bluesky Explainer thread by Dr. Kate Kennedy here:
Publication: “No evidence of immune exhaustion after repeated SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in vulnerable and healthy populations”
Below is an ‘explainer’ thread from Bluesky. See original here
Publication alert: “No evidence of immune exhaustion after repeated SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in vulnerable and healthy populations” @natcomms.nature.com The backstory is particularly interesting-it’s a tale of the conflicting needs of scientists & decision makers in times of disinformation ….1/n
To begin – my team was funded by the CITF to study COVID-19 infections/vaccinations in older adults & people on immunosuppressants. We had a broad mandate to look at ‘cellular & humoral immunity’ and unlike most grants there was a constant feedback to decision makers, participants & the public 2/n https://www.covid19immunitytaskforce.ca/
This meant that I got a pretty good sense of people’s worries and concerns and we could get solid data to address them. Case in point – we provided data that long-term care residents needed a 3rd dose and then a 4th – they got them and colleagues proved they prevented many infections 3/n https://www.bmj.com/content/378/bmj-2022-071502.short
In 2021 internet personalities were fretting that too many vaccines would lead to ‘immune exhaustion’. Most immunologists were not worried (explanation to follow) but I was shocked to hear in meetings that some folks on decision making tables were worried, esp, for vulnerable populations 4/n
What is this scary ‘immune exhaustion’? When you turn on an inflammatory response (e.g., by vaccination/infection) you have to have a way to turn it off. T cells that recognize an antigen multiply, make cytokines and start to express ‘off-switches’ which have names like PD-1, Tim-3 & Lag-3. 5/n
When there is a lot of antigen around (ie. during infection or vaccination) the balance between the on-switch (antigen-stimulation) and the off-switch (PD-1 & friends) favours being on – the T cells expand & differentiate & work their magic. Here PD1 is better described as an ‘activation marker’….. 6/n
…than an exhaustion marker. When the antigen decreases (ie infection or vaccine clears), the off-switches signal that it’s time to close up the inflammatory shop. It is pretty rare that antigens don’t go away but in cancer that chronic stimulation can lead to sustained expression of the PD1 off-switch. 7/n
How do you know when a T cell is truly ‘exhausted’? It expressed these markers AND it loses its function. Here’s where our study shines – we looked at the T cells’ ability to produce at least 1 cytokine (‘functionality’) or more than 1 cytokine (‘polyfunctionality’). 8/n
Repeat vaccination does not affect the T cells ability to make cytokines, even in vulnerable populations. They may express some activation markers but they are definitely not turned off. 9/n
Pity the lead author, PhD student @jennabenoit.bsky.social Her committee would grill her ‘why are you doing this- we all know vaccines don’t cause exhaustion!’ She held strong “Because policymakers & the public need us to PROVE this in THESE people”-She was strong, thorough & committed. 10/n
So why do so many people make such rash statements on whether a T cell is doing it’s thing (PD-1 = activation) vs crashing out (PD-1 =exhausted)? Above I said this disinformation began circulating in 2021 – we’ve been working on this story since then 11/n
Measuring 1 marker (eg PD1) and making wild inferences is relatively cheap & quick but measuring T cell function and analyzing these complex data is slow & expensive. Indeed we had a team of people working very hard in a clinical trials quality immune testing lab and an analysis team to generate these data. 12/n
https://healthresearch.healthsci.mcmaster.ca/single-cell-spatial-profiling-core-facility/human-immune-monitoring-services/
Learnings: Disinformation = quick to make up but hard to disprove and even immunologists and experts can have seeds of doubt sown by bad actors. Vulnerable populations deserve to be included in research. Negative data studies are impt but hard to sell (see reviews of the paper!). 13/n
Huge shout out to lead author @jennabenoit.bsky.social and the not-on-Bluesky team from our star phlebotomist/blood processor Braeden Cowbrough, flow cytometry genius Dr. Jessica Breznik, analytics guru Dr. Chris Verschoor, and HITS Team (Nichols, Hagerman, Bramson) and of course our participants. 14/14